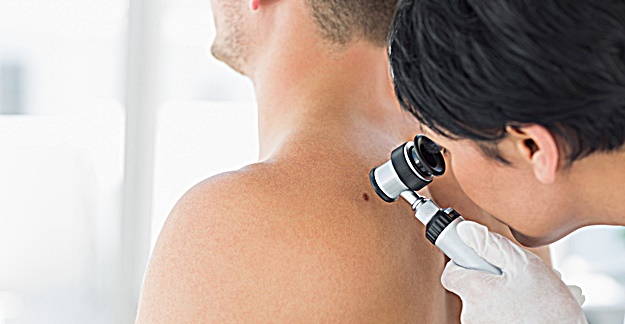
Drugs that treat erectile dysfunction (ED), like Viagra (sildenafil), do not increase the risk of developing a kind of deadly melanoma, according to a large meta-analysis that looked at more than 866,000 men that had taken the medications.
The report, published in the Journal of the National Cancer Institute, is significant in that it came to a different conclusion than a 2014 JAMA Internal Medicine study that did find a link between sildenafil and a higher melanoma risk. The publication of that study prompted the FDA last year to put Viagra and other PDE5 inhibitors such as Cialis (tadalafil) and Levitra (vardenafil) on a watch list of drugs with potential safety issues.
In the new meta-analysis that examined 5 large clinical trials of men that took a PDE5 inhibitor and melanoma risk, researchers did find that men who took an ED drug had an 11% higher risk of developing melanoma. But they also found the men who took large amounts of ED drugs had no significant increase in melanoma risk, while men with little exposure to them had an elevated risk.
As to why this is the case, researchers attribute the increased risk in some ED users to what is known as “detection bias.” This means that some of the men who took PDE5 inhibitors are more health conscious and more likely to see their physician, and therefore more likely to get diagnosed with melanoma.
“Overall, Viagra and other PDE5 inhibitors are safe medications as long as men are not taking nitrates, which carry a risk of reducing blood pressure,” lead author Stacy Loeb, MD, a urologist at NYU Langone Medical Center, said in a statement. “Physicians and patients should not be concerned about taking these medications on account of worry about melanoma.”