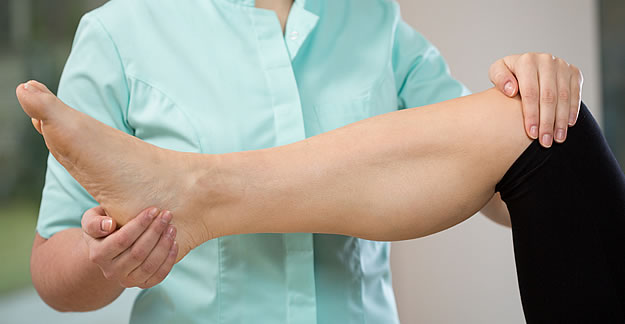
Most patients who undergo anterior cruciate ligament (ACL) surgery typically do not require pain medication 3 months after the procedure. However, researchers found that patients who were filling opioid prescriptions before surgery were 10 times more likely to be filling prescriptions 5 months after surgery.
In the paper presented at the American Orthopedic Society for Sports Medicine’s Annual Meeting on July 22, researchers showed a link between pre-operative opioid use and a post-operative continuation of opioid use long after non-opioid users stopped their pain meds.
Chris A. Anthony, MD, lead researcher from the University of Iowa Hospitals and Clinics, in Iowa City and his colleagues identified 4,946 arthroscopic knee surgeries that were performed and documented in the Humana Inc. database between 2007-2017. They evaluated the effect of preoperative opioid demand on postoperative drugs demand by comparing those who did and did not fill prescriptions pre-and post-surgery. Patients were considered preoperative opioid users if they had filled a prescription in the 3 months preceding surgery.
The results, cited in a report from the conference, showed that nearly 7% of patients were still filling opioid prescriptions 3 months after surgery, with almost 5% still filling prescriptions at 12 months. Patients younger than 25 years of age were 4 times as likely to be filling opioid prescriptions 9 months after surgery.
“We hope that our research will help contribute additional information to the baseline this medication demand data and continue to increase our knowledge of how to better cope with addiction and pain management following surgery,” said Anthony.