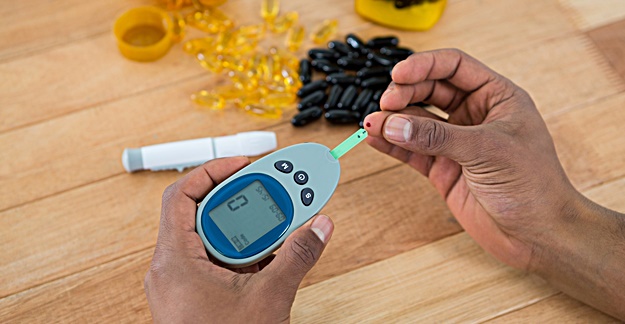
The newest class of diabetes drugs on the market may increase a patient’s risk for developing a serious complication and ketoacidosis that can potentially be fatal.
Researchers found that type 2 diabetes patients taking SGLT2 inhibitors – which include Farxiga (dapagliflozin), Invokana (canagliflozin) and Jardiance (empagliflozin) – were twice as likely to experience diabetic ketoacidosis compared to people who were taking another type of diabetes medication. In diabetic ketoacidosis, a patient has high levels of acids known as ketones in the blood. Symptoms include vomiting, abdominal pain, shortness of breath and brain swelling.
Researchers came to their conclusion after looking at 40,000 people taking an SGLT2 inhibitor, and then comparing results to those on a DPP-4 inhibitor. Drugs in the latter group include Januvia (sitagliptin), Onglyza (saxagliptin) and Tradjenta (linagliptin).
After 180 days, 26 patients taking a DPP-4 inhibitor were diagnosed with diabetic ketoacidosis compared to 55 individuals taking SGLT2 inhibitors, they reported in the New England Journal of Medicine. Study authors, however, noted that the rate of ketoacidosis is still very small with SGLT2 inhibitors.
“This is a side effect that’s usually seen in patients with type 1 diabetes mellitus – not type 2 – so doctors are not ‘on the lookout’ for it,” lead author Michael Fralick, MD, of Boston’s Brigham and Women’s Hospital, said in a statement. “That means that the risk of this side effect might actually be even higher than what we found due to misdiagnosis/under recording.”